Authors: Anthony M. Wanjohi1 and Peter Gichini2
1,2Kenya Projects Organization
P.O. Box 15509-00503, Mbagathi, Nairobi-Kenya
Corresponding Author Email: wanjohi@kenpro.org
Agriculture plays a pivotal role in Kenya’s economy, providing livelihoods for a significant portion of the population and contributing to the country’s food security. In recent years, there has been growing interest in integrating renewable energy technologies into Kenya’s agricultural sector. This integration aims to enhance productivity, improve energy access, and promote sustainability. Kenya’s agricultural sector is diverse, encompassing both small-scale subsistence farming and commercial agriculture. Kenya’s agricultural sector contributes approximately 25% of Kenya’s GDP and employs over 50% of the total labor force (World Bank, 2019). Maize, tea, coffee, horticultural products, sugarcane, and livestock are among the key agricultural commodities produced in the country (KNBS, 2020). Sustainable farming methods require affordable and sustainable sources of energy. Thus, renewable sources of energy such a solar and biogas are continually gaining grounds in farming in Kenya. This article provides an overview of innovative application of Solar and Biogas in Agriculture in Kenya’s context.
Introduction
The integration of renewable energy technologies in Kenya’s agricultural sector presents numerous opportunities. It can enhance agricultural productivity, improve energy access for farmers, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and address environmental sustainability. Two prominent renewable energy sources in this context are solar energy and biogas energy.
Solar energy is abundant in Kenya due to its favorable climatic conditions, offering significant potential for agricultural applications. Solar-powered irrigation systems have gained traction, providing reliable water sources for irrigation and reducing dependence on unpredictable rainfall patterns (Yadaiah et al., 2020). Solar-powered pumps, solar dryers, and solar-powered agro-processing equipment are also being used to increase productivity and add value to agricultural products (Mafuta et al., 2019).
Biogas technology also presents another renewable energy option for Kenya’s agricultural sector. Biogas digesters, which convert organic waste into biogas and bio fertilizers, have multiple benefits. Biogas can be utilized for cooking, heating, and electricity generation, addressing energy needs in rural areas (Nzila et al., 2017). Additionally, the byproduct, bio fertilizer, enhances soil fertility and improves crop yields (Mbuge et al., 2016).
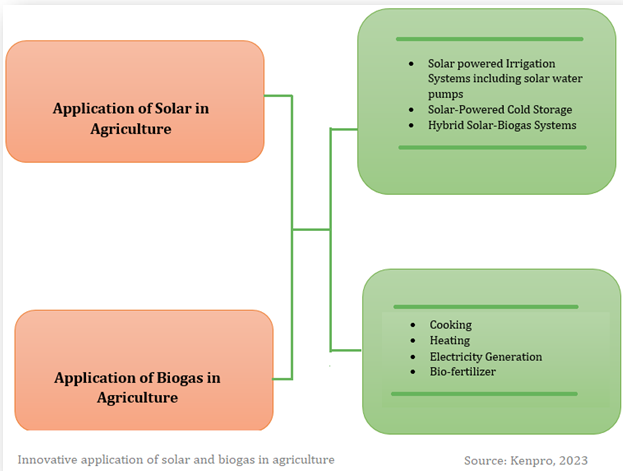
In Kenya’s agricultural sector, the integration of solar energy and biogas technologies has gained prominence as part of efforts to enhance sustainability and energy access. The country’s abundant sunlight makes solar power an attractive option for various agricultural activities, such as irrigation and farm machinery. Additionally, biogas technology has provided farmers with a renewable energy source derived from organic waste, reducing reliance on firewood and charcoal while addressing waste management challenges. These technologies have led to increased productivity, higher incomes, and rural electrification in remote areas. Furthermore, by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting clean energy solutions, Kenya’s adoption of solar and biogas technologies align with its environmental conservation objectives. Overall, integrating solar and biogas technologies into Kenya’s agricultural background demonstrates a commitment to sustainable development, energy efficiency, and environmental stewardship. The figure below shows innovative application of solar and biogas in agriculture.
Innovative Application of Solar in Agriculture
In Kenya, innovative approaches are being developed to integrate solar energy and biogas technologies into farming practices, offering numerous benefits for agricultural productivity, energy access, and environmental sustainability. Figure 1 shows innovative application of solar and biogas on integrated farming.
Solar-Powered Irrigation Systems: Solar-powered irrigation systems are being implemented to address the challenge of water scarcity and unreliable electricity supply. These systems utilize solar panels to power pumps (Solar water pumps), providing a reliable and sustainable source of energy for irrigation. This innovation allows farmers to have better control over water availability, enabling year-round cultivation and improving crop yields.
Solar-Powered Cold Storage: In remote agricultural areas with limited access to electricity, solar-powered cold storage solutions have emerged as a game-changer. These systems use solar energy to power refrigeration units, enabling farmers to store and preserve perishable produce such as fruits, vegetables, and dairy products. Solar-powered cold storage helps reduce post-harvest losses and extends the shelf life of agricultural goods, allowing farmers to access better markets and command higher prices.
Hybrid Solar-Biogas Systems: Hybrid systems that combine solar energy and biogas technologies are being explored to maximize the benefits of both renewable energy sources. These integrated systems leverage the complementary nature of solar and biogas energy production. Solar power is utilized during the day when sunlight is abundant, while biogas fills the energy gap during periods of low solar availability, such as at night or during cloudy days. This involves use of biogas generators. This innovation ensures a continuous and reliable energy supply for various farming activities.
Innovative Application of Biogas in Agriculture
Biogas for Cooking: Biogas can replace traditional wood or charcoal stoves for cooking purposes. This reduces the reliance on deforestation and provides a cleaner and more efficient energy source for cooking meals.
Electricity Generation: One of the innovative applications is the generation of electricity from biogas using biogas generator. This electricity can power farm equipment, lighting, and other electrical appliances, reducing reliance on the grid and lowering energy costs for farmers.
Heating: Biogas can be used for space heating during colder seasons, providing a cost-effective and eco-friendly way to maintain comfortable temperatures in farm buildings.
Biofertilizer: Biogas digesters not only produce biogas but also generate valuable byproducts, one of which is biofertilizer.
In summary, the innovative application of biogas in agriculture extends beyond energy generation to include the production of biofertilizer. This biofertilizer not only enriches the soil and enhances crop productivity but also promotes sustainable and eco-friendly farming practices, benefiting both farmers and the environment.
Conclusion
The integration of solar energy and biogas technologies into Kenya’s agricultural sector is a testament to the nation’s commitment to sustainable development. Through innovative solutions such as solar-powered irrigation, cold storage, and biogas digesters, the agricultural landscape is being revolutionized. These technologies not only enhance productivity and improve energy access but also align with environmental conservation objectives, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting cleaner energy alternatives. By embracing these advancements, Kenya is fostering a more resilient, efficient, and environmentally friendly agricultural sector that benefits both farmers and the country as a whole. Further, integrating solar energy and biogas for farming in Kenya demonstrate the country’s commitment to sustainable agriculture, energy access, and rural development. By harnessing the power of renewable energy sources, farmers can enhance productivity, reduce operating costs, and contribute to a greener and more resilient agricultural sector.
References
Kenya National Bureau of Statistics (KNBS). (2020). 2019 Kenya Population and Housing Census Volume IV: Distribution of Population by Socio-Economic Characteristics. Retrieved from https://www.knbs.or.ke/download/volume-iv-distribution-of-population-by-socio-economic-characteristics/
Mafuta, M. E., Muhonja, C. N., & Wekesa, E. W. (2019). Solar Crop Dryer Design and Development: A Case Study of Smallholder Farmers in Vihiga County, Kenya. Journal of Energy Research and Reviews, 2(1), 1-9.
Nzila, C., Mwirichia, R., & Mbui, D. (2017). Performance Evaluation of a Small-Scale Biogas Digester for Co-Digestion of Agricultural Wastes in Nairobi, Kenya. International
Sovacool, B. K., Kryman, M., & Smith, T. (2015). Scaling and commercializing mobile biogas systems in Kenya: a qualitative pilot study. Renewable Energy, 76, 115-125.
World Bank. (2019). Kenya Economic Update: Creating Opportunities for the Rural Economy. Retrieved from https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/31487/9781464813854.pdf
Yadaiah, N., Nuthalapati, M., & Garg, A. (2020). Solar Pumping System for Sustainable Irrigation: A Case Study in Kenya. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Renewable Energy Technologies (pp. 169-179). Springer. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-13-8797-6_15
For inquiries about innovative application of Solar and Biogas in Agriculture, kindly contact KENPRO Support Team or call us +254725788400.