By Anthony M. Wanjohi:
Project life cycle is a project management framework meant to assist project managers to direct project activities from the beginning to the end. The basic phases of project cycle include project identification, planning, implementation, and monitoring and evaluation and termination.
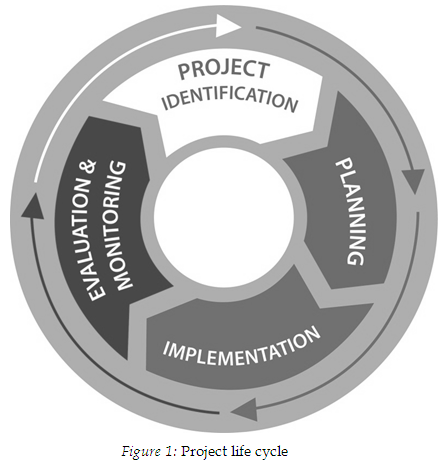
Project Life Cycle
There exist other models of project life cycle. For instance, according to European Union (2002), the stages of a project life cycle include: Programming, Identification, Appraisal, Financing, Implementation, and Evaluation. However, most common and fundamental project life cycle stages include Identification, Planning, Implementation, Evaluation and Termination. See Figure 1.
Project Identification
Within the programme framework, problems, needs and interests of possible stakeholders are analysed (problem analysis); project ideas and other actions are identified and screened.
The outcome of the process is a decision on whether or not the options developed should be undertaken.
Project Planning
Project planning defines the project general objective, project activities and implementation framework. It guides project team through the phases of implementation and closure.
The basic process of project planning entails the following: Defining project objectives, project output, and project activities; drawing project implementation matrix; providing risk management roadmap and budget planning.
Implementation
This is a stage where the set resources are used to carry out the planned project activities, within given timeline and the responsible or actors.
It is about putting the resources into use: Personnel, Finance, Materials and Equipment. It entails
Monitoring and Evaluation
Monitoring
Project monitoring is a continuous and periodic review, and overseeing of the project to ensure: Input deliveries, work schedules, target outputs and other required actions proceed according to the project plan.
To assess the progress of a project, continuous monitoring of project activities is necessary. This helps the project team to make adjustments given the changing circumstances.
Evaluation
This is a process that involves systematic collection, analysis and interpretation of project related data that can be used to understand how the project is functioning in relation to the project objectives:
Evaluation as an assessment of the project’s achievements and impact; it examines the relevance and fulfillment of objectives, efficiency, effectiveness, impact and sustainability.
Evaluation leads to a decision to continue, change or stop a project, and its conclusions are taken into account when planning and implementing similar projects.
Project Termination
The project implementation cycle is treated as complete with the termination of the project. Literally termination means “ending” and in the context of project implementation, it spells out one of the three meanings:
Normal termination: when a project is terminated within the stipulated resources and time.
Early termination: Early termination can occur due to change of policy, and programs of the concerned organizations or unforeseen project risks.
Late termination: Late termination is generally attributed to factors such as time and cost overruns.
About the Author
Wanjohi, AM is the founder and Director of Projects and Research at KENPRO. He is a Monitoring, Evaluation, Research and Learning (MERL) specialist.
Bibliography
European Commission (2002). Project Cycle Management handbook. Freiburg: PARTICIP
Suggested Citation
Wanjohi, A.M. (2020). Project Planning and Management Handbook. Nairobi: Kenpro Publications